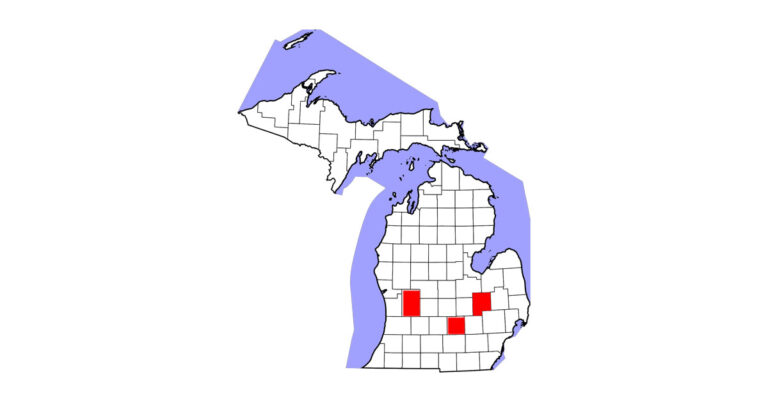
The Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development has reported two new strangles cases in the state.
A 10-year-old Tennessee Walking Horse gelding in Livingston County presented with a fever and nasal discharge on June 12. He was unvaccinated and is currently recovering in voluntary quarantine.
A 10-year-old Standardbred mare in St. Joseph County presented with an abscess on June 12. She is also reported to be unvaccinated and recovering in voluntary quarantine.
EDCC Health Watch is an Equine Network marketing program that utilizes information from the Equine Disease Communication Center (EDCC) to create and disseminate verified equine disease reports. The EDCC is an independent nonprofit organization that is supported by industry donations in order to provide open access to infectious disease information.

Read More: Climate Change and Horse Health
About Strangles
Strangles in horses is an infection caused by Streptococcus equi subspecies equi and spread through direct contact with other equids or contaminated surfaces. Horses that aren’t showing clinical signs can harbor and spread the bacteria, and recovered horses remain contagious for at least six weeks, with the potential to cause outbreaks long-term.
Infected horses can exhibit a variety of clinical signs:
- Fever
- Swollen and/or abscessed lymph nodes
- Nasal discharge
- Coughing or wheezing
- Muscle swelling
- Difficulty swallowing
Veterinarians diagnose horses using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing with either a nasal swab, wash, or an abscess sample, and they treat most cases based on clinical signs, implementing antibiotics for severe cases. Overuse of antibiotics can prevent an infected horse from developing immunity. Most horses make a full recovery in three to four weeks.
A vaccine is available but not always effective. Biosecurity measures of quarantining new horses at a facility and maintaining high standards of hygiene and disinfecting surfaces can help lower the risk of outbreak or contain one when it occurs.